Yxue F
And g(z) = ey cosxiey sinx Using the CauchyRiemann equations, prove that f is entire, but g is nowhere holomorphic.

Yxue f. All of Six Sigma can be summarized with what’s called the breakthrough equation — one generalpurpose equation that shouldn’t intimidate even the least mathematically inclined Y = f(X) ε, where Y is the outcome(s) or result(s) you desire or need X represents the inputs, factors, or pieces necessary to create the outcome(s) You can. Proof lnexy = xy = lnex lney = ln(ex ·ey) Since lnx is onetoone, then exy = ex ·ey 1 = e0 = ex(−x) = ex ·e−x ⇒ e−x = 1 ex ex−y = ex(−y) = ex ·e−y = ex · 1 ey ex ey • For r = m ∈ N, emx = e z }m { x···x = z }m { ex ···ex = (ex)m • For r = 1 n, n ∈ N and n 6= 0, ex = e n n x = e 1 nx n ⇒ e n x = (ex) 1 • For r rational, let r = m n, m, n ∈ N. Nov 16, 18 · Thanks for contributing an answer to Mathematics Stack Exchange!.
Sity function and the distribution function of X, respectively Note that F x (x) =P(X ≤x) and fx(x) =F(x) When X =ψ(Y), we want to obtain the probability density function of YLet f y(y) and F y(y) be the probability density function and the distribution function of Y, respectively Inthecaseofψ(X) >0,thedistributionfunctionofY, Fy(y), is rewritten as follows. E(var(yx)) = e(e(y2x)) e(e(yx)2) We have already seen that the expected value of the conditional expectation of a random variable is the expected value of the original random variable, so applying this to Y 2. F v= @f @v = @f @x @x @v @f @y @y @v f u= (2x y)(v) (x 2y)(1 v) = 2uv2 2u 2u v2 f v= (2x y)(u) (x 2y)(u v2) = 2u2v 2u2 v3 f x= 2x y= 2uv u v So, 2xf x= 2uvf x.
Definition of Partial Derivatives Let f(x,y) be a function with two variables If we keep y constant and differentiate f (assuming f is differentiable) with respect to the variable x, using the rules and formulas of differentiation, we obtain what is called the partial derivative of f with respect to x which is denoted by Similarly If we keep x constant and differentiate f (assuming f is. In this equation, both f (x) f (x) and g (x) g (x) are functions of one variable Now suppose that f f is a function of two variables and g g is a function of one variable Or perhaps they are both functions of two variables, or even more How would we calculate the derivative in these cases?. Where b is a positive real number, and the argument x occurs as an exponent For real numbers c and d, a function of the form () = is also an exponential function, since it can be rewritten as = () As functions of a real variable, exponential functions are uniquely characterized by the fact that the growth rate of such a function (that is, its derivative) is directly proportional to the.
N d à y Ï 35 þ ï k d JOREDO#KRVKLQRUHVRUW FRP RVKLQR 5HVRUWV 3UHVV 5HOHDVH ñ Q y b 7 b 7 ý c Ð b 7 u ' !. Y= ˆ p 2 sin ;. Sep 12, 18 · In the section we will take a look at higher order partial derivatives Unlike Calculus I however, we will have multiple second order derivatives, multiple third order derivatives, etc because we are now working with functions of multiple variables We will also discuss Clairaut’s Theorem to help with some of the work in finding higher order derivatives.
Homework 8 1 Let Xand Y be independent and identically distributed where Xhas density f X(x) = 1 x2 I(x>1) Let U= X=Y, V = X Find the joint density for (U;V). I v ¶ þ , æ & " , N d à y Ï. Please be sure to answer the questionProvide details and share your research!.
F dS for vector eld F = xi yjz4k and the oriented surface Sthat is the part of the cone z= p x2 y2 beneath the plane z= 1 with downward orientation In other words, nd the ux of F across S Using spherical coordinates, the cone is expressed as x= ˆ p 2 cos ;. QA forum can get you clear solutions for any problem Thousands of. F(x,y) e ху 3 f(xy)=.
P r o t e c t Y o u r s e l f P r o t e c t Y o u r P a r t n e r T H e fa c T s • Bacterial vaginosis (back TEER ee el / va gin NO sus) (BV) is a condition in which there is an overgrowth of some kinds of bacteria in the vagina BV can cause symptoms such as vaginal discharge • BV is common in women of childbearing age. SAMPLE PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS 3 Integrating u xwith respect to y, we get v(x;y) = exsiny eysinx 1 2 y 2 A(x);. F X(x) = F(x) = P(X x) A cdf has three properties 1 F is rightcontinuous At each x, F(x) = lim n!1F(y n) = F(x) for any sequence y n!xwith y n>x 2 Fis nondecreasing If x.
Since 0 = u xy u x = (u y u) x, we can integrate at once with respect to xto obtain u yu= f(y)This is a rst order linear \ODE" in the variable y Introducing the integrating factor = exp R 1dy = ey, it becomes @y (e yu) = ef(y) Integrating with respect to ythis time yields. A l l y x e h O u t f i t s 434 likes · 2 talking about this Ropita de segunda a muy buen precio y de buena Calidad Por el momento solo entregas personales en CD Cuauhtemoc, Ecatepec,. Dec 31, 17 · Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange.
Y' is a solution of xu' = 3u whose general solution is u(x) = Cx^3 (found via a separation of variables) so y(x) = Cx^4 D\\ CD = 1\\ 16C D = 2 then, y(x) = \frac 1{15} (x^4 14) y ′ is a solution of x u ′ = 3 u whose general solution is u ( x ) = C x 3 (found via a separation of variables) so y ( x ) = C x 4 D C D = 1 1 6 C D. Theorem 161 If f is analytic in a domain D and f(xiy) = u(x,y)iv(x,y), then u and v are harmonic in D Proof The result follows from the discussion above combined with a result we will prove later if f is analytic at z 0 = x 0 iy 0, then u and v have continuous partial derivatives of all orders at (x 0,y 0) Example 161 We know that f. E n c l o s u r e ( s ) ( U ) E n c l o s e d f o r N S L B a n d I I S ar e t h e following O n e c o p y o f a g f i r i P B o f e m a i l s (3 p a g e s ) f g i n c l u d e an e m a il fro m FBIHQ , C T D , d allefl L W /2 1 /2 0 0 5 to A SC , e t a l, b l b 6 b 7 C b 2 b 7 E D e ta ils (R' sclL aiL x i.
U E F d b ł̂ ₢ 킹 TEL V V s \ 414. F x ∂ ∂ is the slop of the tangent drawn to the curve of intersection of the surface z = f(x, y) with a plane parallel to the plane y = 0 Further, in general f x ∂ ∂ and f y ∂ ∂ are functions of both x and y and, therefore can be differentiated for higher order derivatives with respect to x or y Thus 22 2xx yx,, ff f f ff xx xy xyx. (x;y) 2Rg What it says is that for every pair (x;y) in R, you take it,.
X= f(x) This is an ODE for uin the xvariable, which one can solve by integrating with respect to x, arriving at at the solution u(x;y) = F(x) G(y) 13 Conclusion Notice that where the solution of an ODE contains arbitrary constants, the solution to a PDE contains arbitrary functions. Facing hyperbolic segments as well as the union of the lines y = x and y = x Hence, the solution u is uniquely determined on the set where x2 y2 0 In our previous notation, this means that we can determine the constant C and the functions g 1 and g 2, but the functions h 1 and h 2 cannot be determined from the given data. Solution for Find f(x,y) and fy(x,y) Then, find fx (2, 3) and fy(1,3) 2ху?.
This video is Part 1 of the Alphabet ABC Phonics Series, covering letters A, B, C, D, E, F, and GThis series goes through each of the letters, starting with. Bility density function (pdf) of a function of the random variable X Suppose Y = We begin with the cumulative distribution function of Y F Y(y) = P(Y y) = P( y) = P(X y 1 n) So far we have F Y(y) = F X(y 1 n) To nd the pdf of Y we simply di erentiate both sides wrt to y f Y(y) = 1 n y1 n 1 f X(y 1 n) where, f X() is the pdf of X. 63 Expected value If X and Y are jointly continuously random variables, then the mean of X is still given by EX = Z ∞ −∞ xfX(x)dx If we write the marginal fX(x).
The two points, which has gradient –y=–x, is a good approximation to the tangent line at (x;y) which has gradient dy=dx This means that –y=–x dy=dx so that –y (dy=dx)–x We want to generalise this idea to a function z = f(x;y) of two variables, whose graph will be a surface. F rs = 2 s Therefore, f rss = 2 s2;. Where A(x) is an arbitrary function of x On the other hand, integrating u y with respect to x, we have.
Y x y2 (18) Without giving the working it is not difficult to show that the CR equations hold everywhere except at the origin z= 0 where the limit is indeterminate z= 0 is the point where it fails to be differentiable Hencew= z−1 is analytic everywhere except at z= 0 Example 3 f(z) = z2 We have u(x,y) = x2 y2, v(x,y) = 0, (19. X&Y is the third studio album by the British rock band ColdplayIt was released on 6 June 05 by Parlophone in the United Kingdom, and a day later by Capitol Records in the United States The album was produced by Coldplay and producer Danton SuppleIt is noted for its troubled and urgent development, with producer Ken Nelson having originally been tasked with producing much of. F rst = 0 Determine whether each of the following functions is a solution of Laplace’s equation u xx u yy = 0 (a) u = x2 y2, (b) u = x2 y2, (c) u = x3 3xy2, (d) u = ln p x2 y2, (e) u = sinxcoshy cosxsinhy, (f) u = e x cosy e y cosx (a) not solution, (b) solution , (c) not solution, (d.
But avoid Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers. FX,Y (x, y) = 0, otherwise In class we have shown the minimum least squares estimate of Y is given by EY X = x (a) Find the least squares estimate of Y given that X = x, for all possible values of x For full credit write the functional form, as opposed to a graph The least square estimate of Y based on X is given by EY X. Solution Integrating with respect to x and treating y as fixed gives f = Z y fixed x2 y 9dx = x3 3 xy 9xA(y), where A is an arbitrary function depending on the fixed variable y ⁄ Example 113 Find the general solution of the PDE, ∂2f ∂x∂y = 2x, where f is a function of two independent variables x and y Solution The PDE can be expressed as.
` F \ A g N u } X ^ Y E I u E U E ` F \ h MASTER OF THE CHAISAW MASTERS OF THE CHAINSAW TOEI ̏ W A S ̖ f ʂ ֎~ ܂. 8 f(x;y) = x2 xy y2;x= uv;y= u=v To show that uf u vf v= 2xf xand uf u vf v= 2yf y we need to nd f u;f v;f xand f y f u= @f @u = @f @x @x @u @f @y @y @u;. Login You must be logged in to read the answer Go ahead and login, it'll take only a minute Login Now.
Z= ˆ p 2 Note that ˚= ˇ=4 We obtain a vector equation r( ;ˆ. ≠ 0willshowthateuev is not harmonic Again, taking u = v = x gives us what we want as e2x is easily seen to be nonharmonic Question 4 (p106 #14) State the domain of analyticity of f(z) = eiz Find the real and imaginary parts u(x,y) and v(x,y) of the function, show that these satisfy the CauchyRiemann equations, and find f′(z) in. If Z = F (X, Y) Where X = Eu Ev, Y = Eu Ev Then Prove that ∂ Z ∂ U − ∂ Z ∂ V = X ∂ Z ∂ X − Y ∂ Z ∂ Y 0 University of Mumbai BE Biomedical Engineering Semester 1 (FE First Year).
If z= f(x,y), where x=euev, y= eu ev show that zu zv=xzx yzy x 3 x y 3 y x 3 x y 3 y x 2 x y 3 y x 3 x y 2 y SUBMIT TRY MORE QUESTIONS View More Questions Solution Solution not clear?. 219 (Canonical Forms) Consider the follwing function f(A,B,C,D) = Σm(0,1,2,7,8,9,10,15) (a) Write this as a Boolean expression in canonical minterm form A B C D. 0 8z 2 C Since f is holomorphic, we have c2 f is holomorphic Now, ff = jfj2 = c2 therefore f = c2 f, which we showed is holomorphic So by Problem 1, f is a constant 5 Consider the two functions f(z) = e y sinx ie y cosx;.
Next About this document THE INTEGRATION OF EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS The following problems involve the integration of exponential functions We will assume knowledge of the following wellknown differentiation formulas. 11 Functions of Two or More Variables A symbol z which has a definite value for every pair of values of x and y is called a function of two independent variables x and y and is written as z = f (x, y) or I (x, y) 12 Limits “The function f (x, y) is said to tend to limit l as x oa and y o b if and only if the limit l is independent of the path followed by the point (x, y) as x o a and y ob. 211 De nition 54 Let Rbe a relation from the set Ato the set BTheinverse relation R 1 from Bto Ais de ned as R 1 = f(y;x) 2B A;.
Obviously the constantzero function mathf(x) = 0/math suffices Also the identity function mathf(x) = x/math works mathf(xy)f(x)f(y) = xy xy = f(xy.
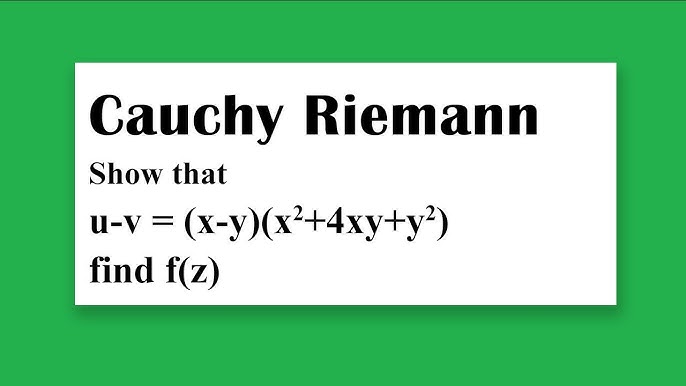
Cauchy Riemann U V E X Cosy Siny Find F X U Iv Youtube

Please Answer Both Part A And B Clearly U 0 1 Find The Pdf Of Y Homeworklib

Solved Can Be Written In The Form Y F Y X Y F Y Chegg Com
Yxue F のギャラリー
What Is The Analytic Function Math F Z Math In Terms Of Math Z Math Whose Real Part Is Math E X X Sin Y Y Cos Y Math Quora
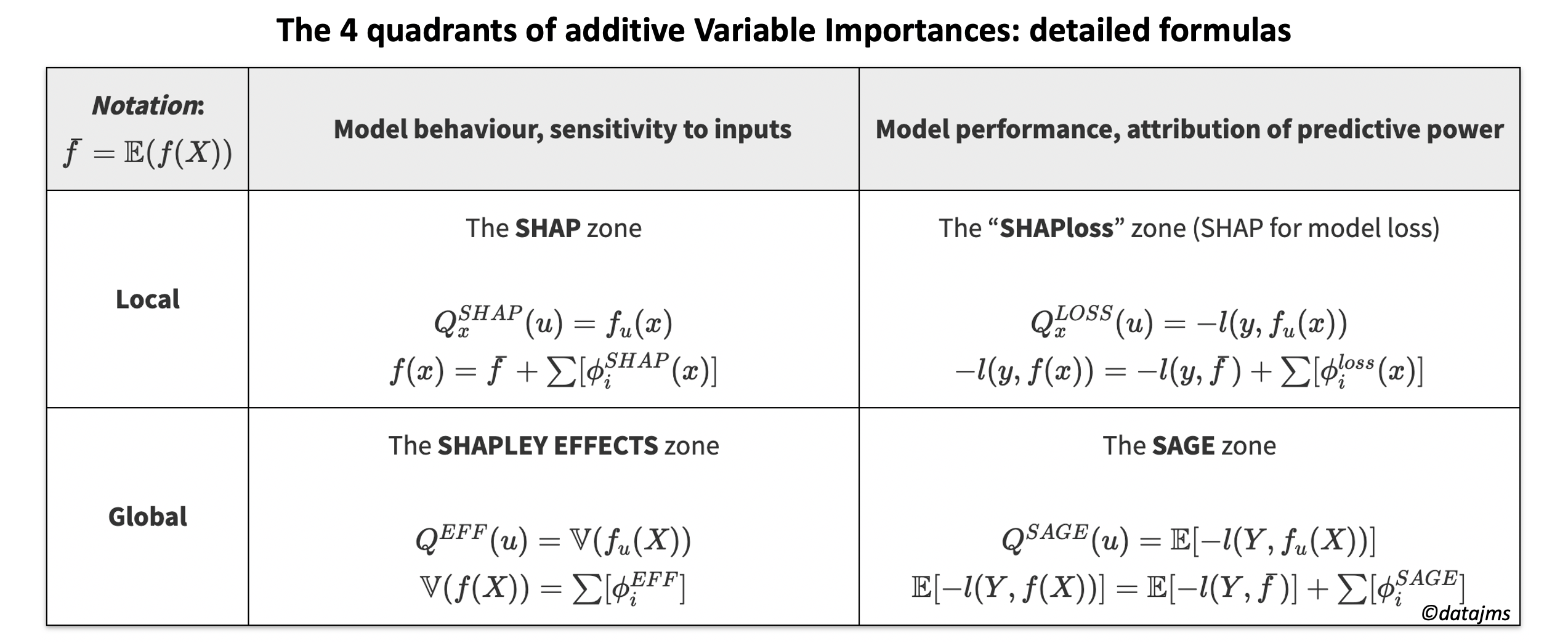
The 4 Types Of Additive Feature Importances By Jean Matthieu Schertzer Towards Data Science

1 Vytah

Answered Q 3 A Suppose U X Y X Y X Y Bartleby

6 Ways To Find The Domain Of A Function Wikihow

Typo A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 3d Neon Fonts Modern Alphabet

A Show That U X Y X X 2 Y 2 Is Harmonic On A Solution U X Y 2 X 2 X 2 Y 2 2 U Course Hero
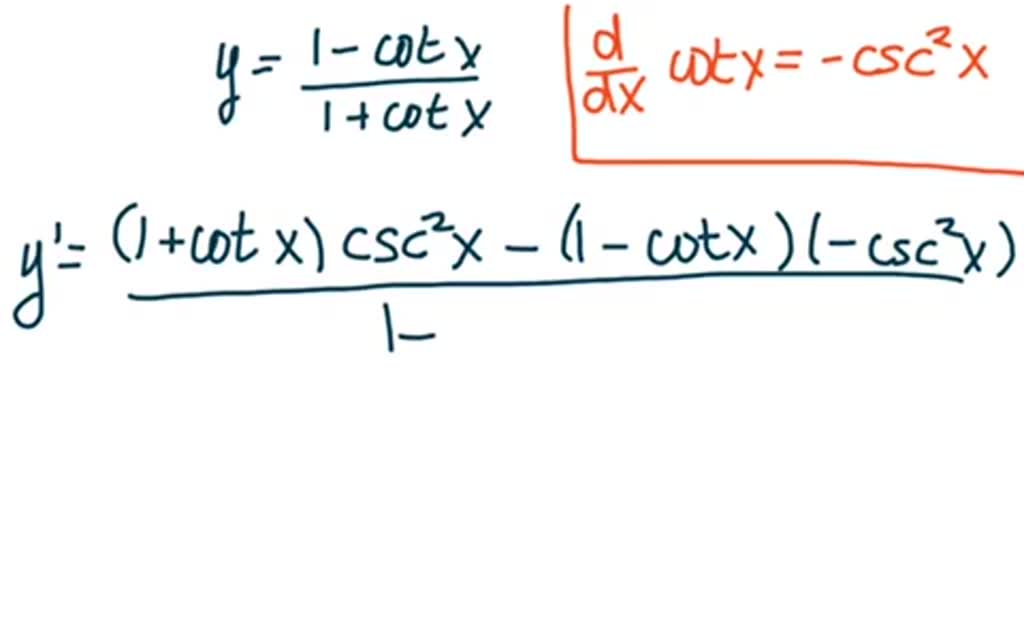
Solved For The Following Exercises Find Frac D
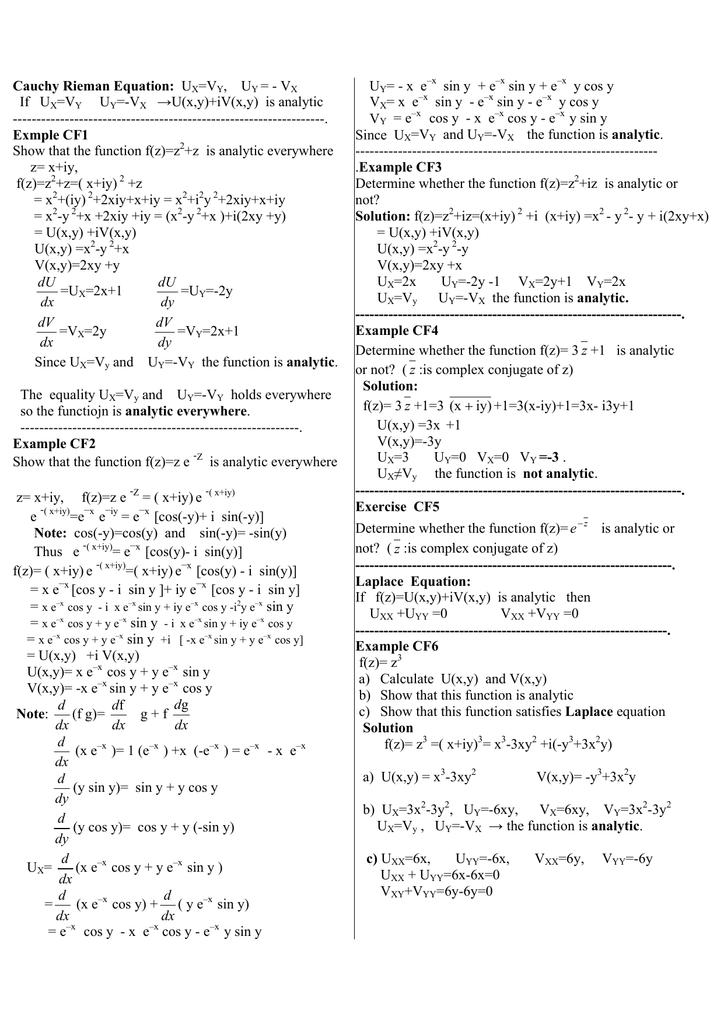
Ux Vy Uy Vx If Ux Vy Uy

Solved Let F U V U V Uv 2 And U U X Y E X Chegg Com

Solved Let F G And H Be Functions Of Two Variables That Chegg Com
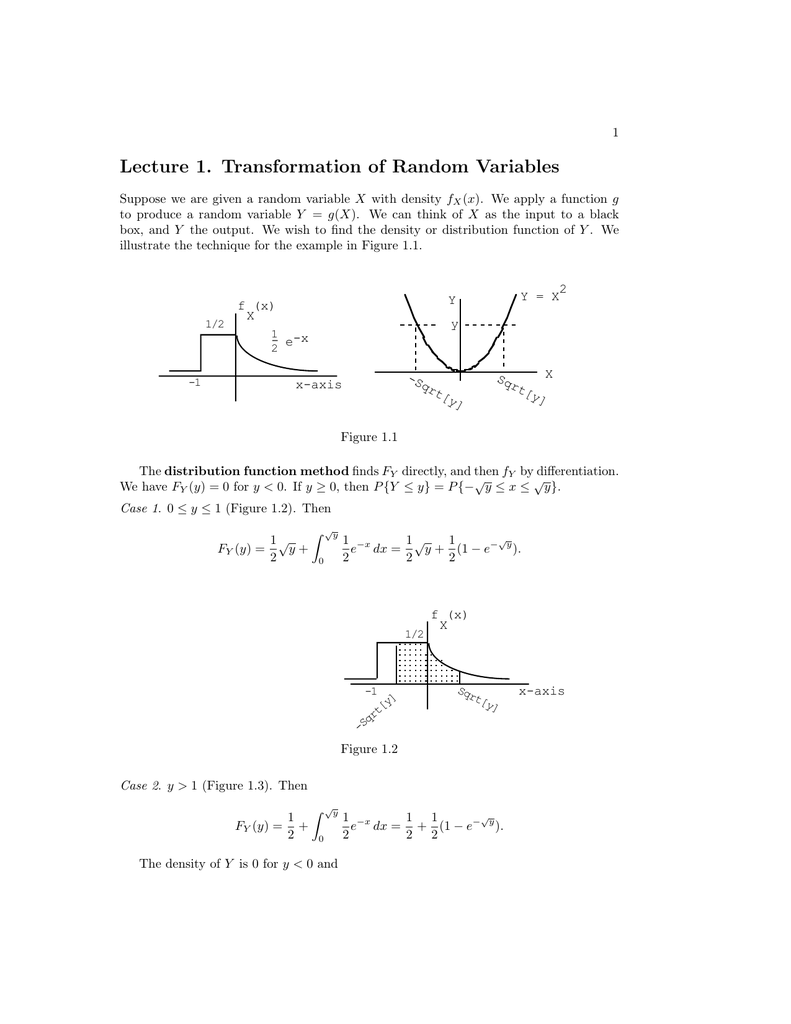
Lecture 1 Transformation Of Random Variables
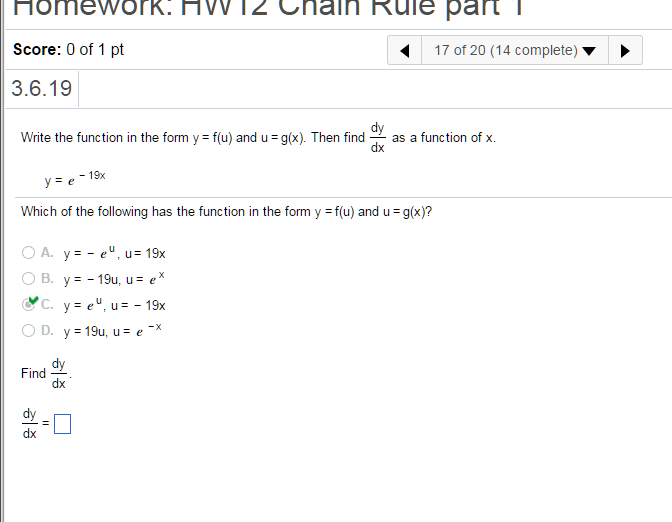
Solved Write The Function In The Form Y F U And U G X Chegg Com
What Is The Analytic Function Whose Real Part Is Y E Xcosy Is The Function Harmonic Quora
If U Log X 2 Y 2 Xy Then X U X Y U Y Is A 0 B U C 2u Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Mcgraw Schaum S Outlines Of Probability Random Variables Random Processes Pages 101 150 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

Jacobians New

Solved Consider The Regression Model Y Bx U E U X Chegg Com

Domain And Range Free Math Help

Calc 501 1000 By James Bardo Issuu
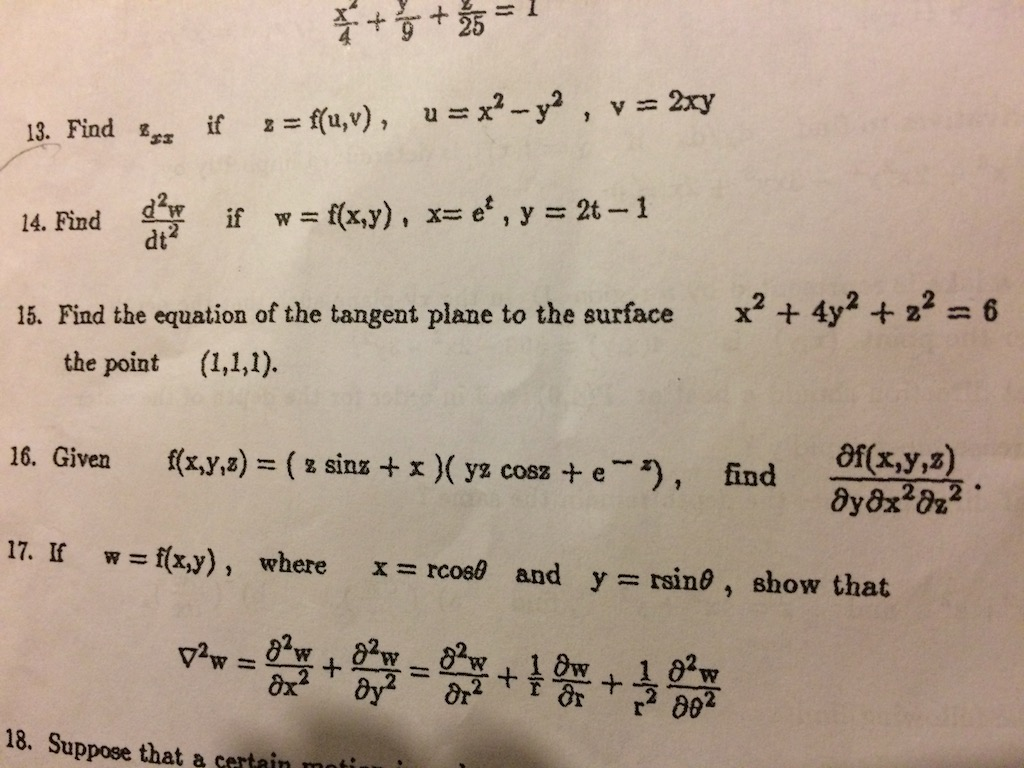
Solved Find Z Xx If Z F U V U X 2 Y 2 V 2xy F Chegg Com

Tutorial Sheet 5 Assignment Studocu

Why V 1 2 Is F Distribution With 2 2 Degree Of Freedom Mathematics Stack Exchange

Let F X Sin Picosx And G X Cos 1pisinx E Two Function Def

Solved Given The Function F X Y With X U V Au Bv Chegg Com

Differential Equations 5410
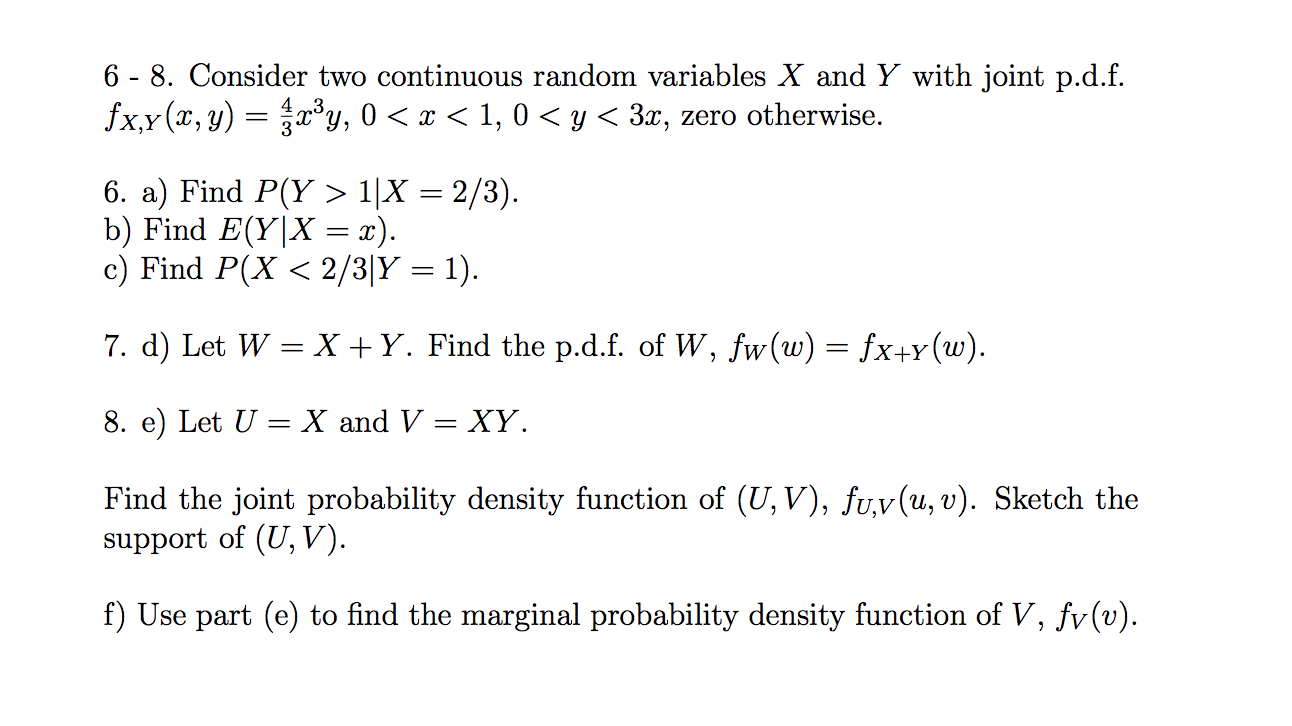
6 8 Consider Two Continuous Random Variables X Chegg Com

Introduction To Partial Differential Equations Pages 1 25 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

On The Stability Of The Heat Equation With An Initial Condition Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub

Solving The Pde Y U X X U Y 1 U 0 Y E Y 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange

Solved The Equation Can Be Written In The Form I E It Chegg Com

The Shaded Area Is Already Covered By C U Is The Unshaded Area In X Download Scientific Diagram
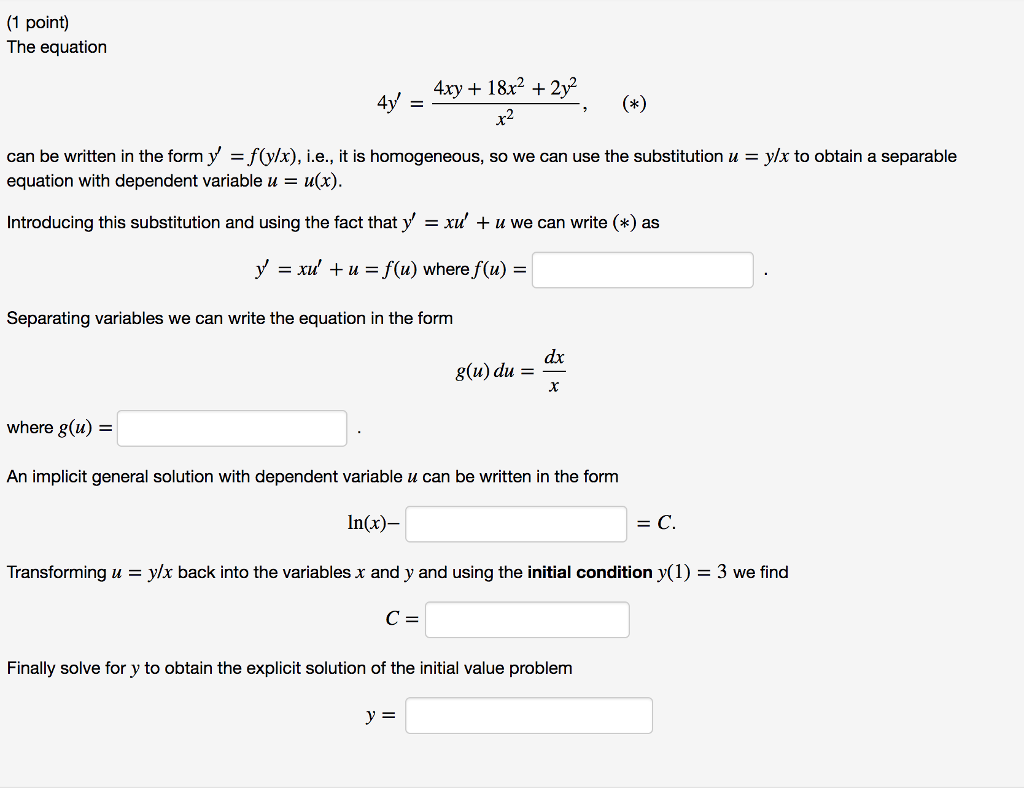
Solved The Equation Can Be Written In The Form Y F Y X Y Chegg Com

Answered 53 58 Find All The Second Partial Bartleby

Answered 8 Write The Function In The Form Y Bartleby

Technical Font Digital Alphabet Letters A B C D E F Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image

Letter Formation Animated Powerpoint And Worksheets Phonics Phonics Jolly Phonics Teaching Handwriting

U Julie 2 U Toni 2 315 Consider The Utility Function U X Y 3 X Y With Mu X 3 Course Hero
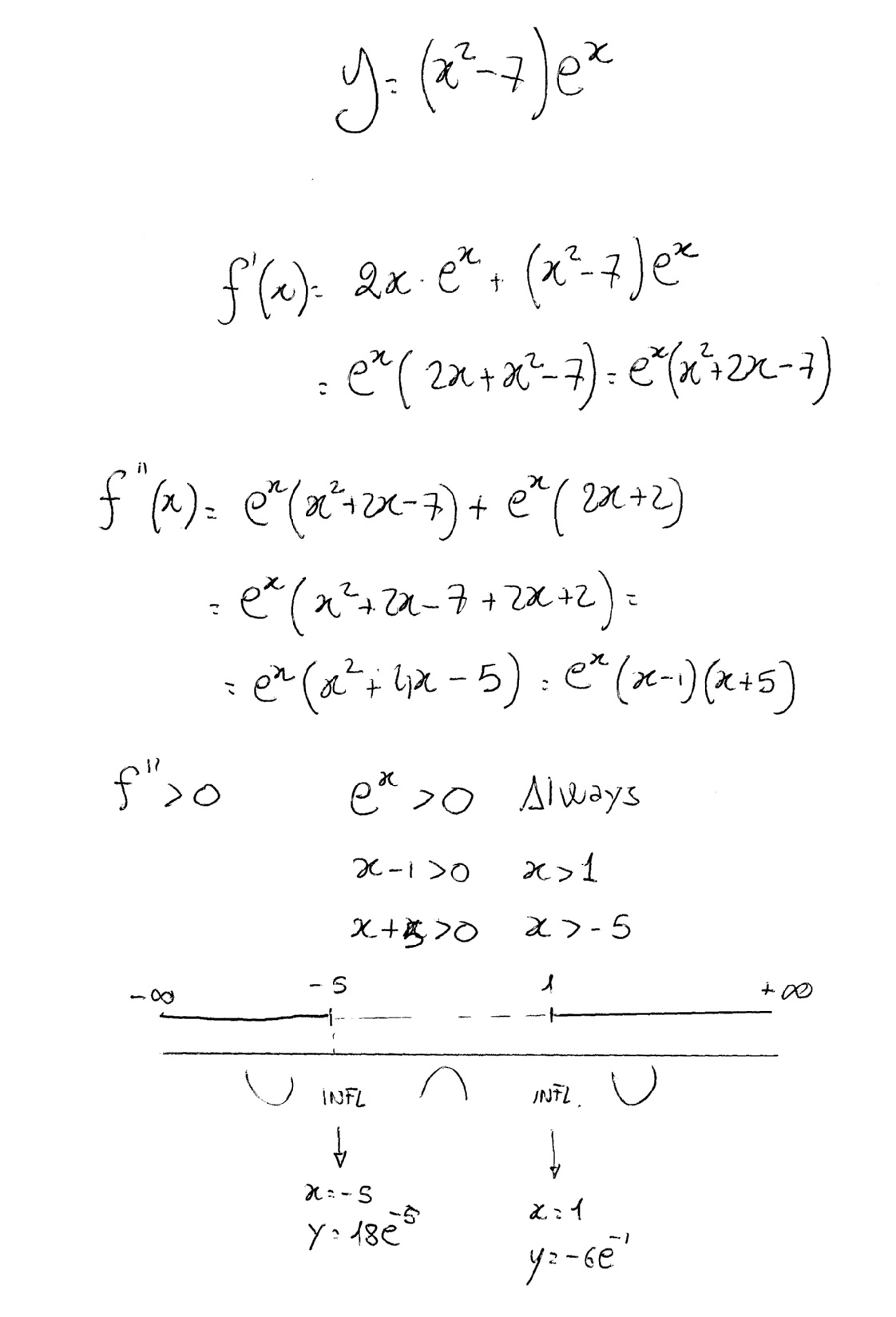
How Do You Determine Intervals On Which The Function Is Concave Up Or Down And Find The Points Of Inflection For Y X 2 7 E X Socratic

Pdf Generalization Of The Famous Riccati And Bernoulli Odes

Partial Differentiation If Z F X Y X E U E V Y E U V Show әz әu әz әv Xәu әx Yәu әy Youtube

The Function F X Y Satisfies The Differential Equation Y Df Dx X Df Dy 0 By Changing To New Variables U X 2 Y 2 And V 2xy Show That F Is In Fact A Function Of

Solving The Pde Y U X X U Y 1 U 0 Y E Y 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
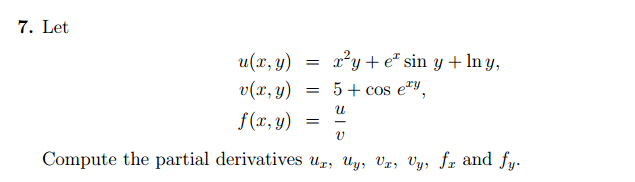
Solved Let U X Y X 2y E X Sin Y Ln Y V X Y 5 Chegg Com

Introduction To Differential Calculus Christopher Thomas Pdf Free Download

A Copy And Complete The Table See How To Solve It At Qanda

Ec212 Tutorial 2 Week 4 With Answers Ec212 Microeconomics Tutorial Week If Studocu

Arzela Ascoli Theorem For Demi Linear Mappings Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub

Question Video Differentiating Compositions Of Exponential And Root Functions Using The Chain Rule Nagwa

Font Stylization Letters Font Composition Logo Rendering Stock Photo Image By C 0123omar
Who Can Solve This Y 2y E X Quora

Part A Ordinary Differential Equations Odes Section 1

Solved Let W X Sin Y X E T Y T 2 Find Dw Dt By U Chegg Com

Let F X Sin Picosx And G X Cos 1pisinx E Two Function Defined

Solved Let F G And H Be Functions Of Two Variables That Chegg Com
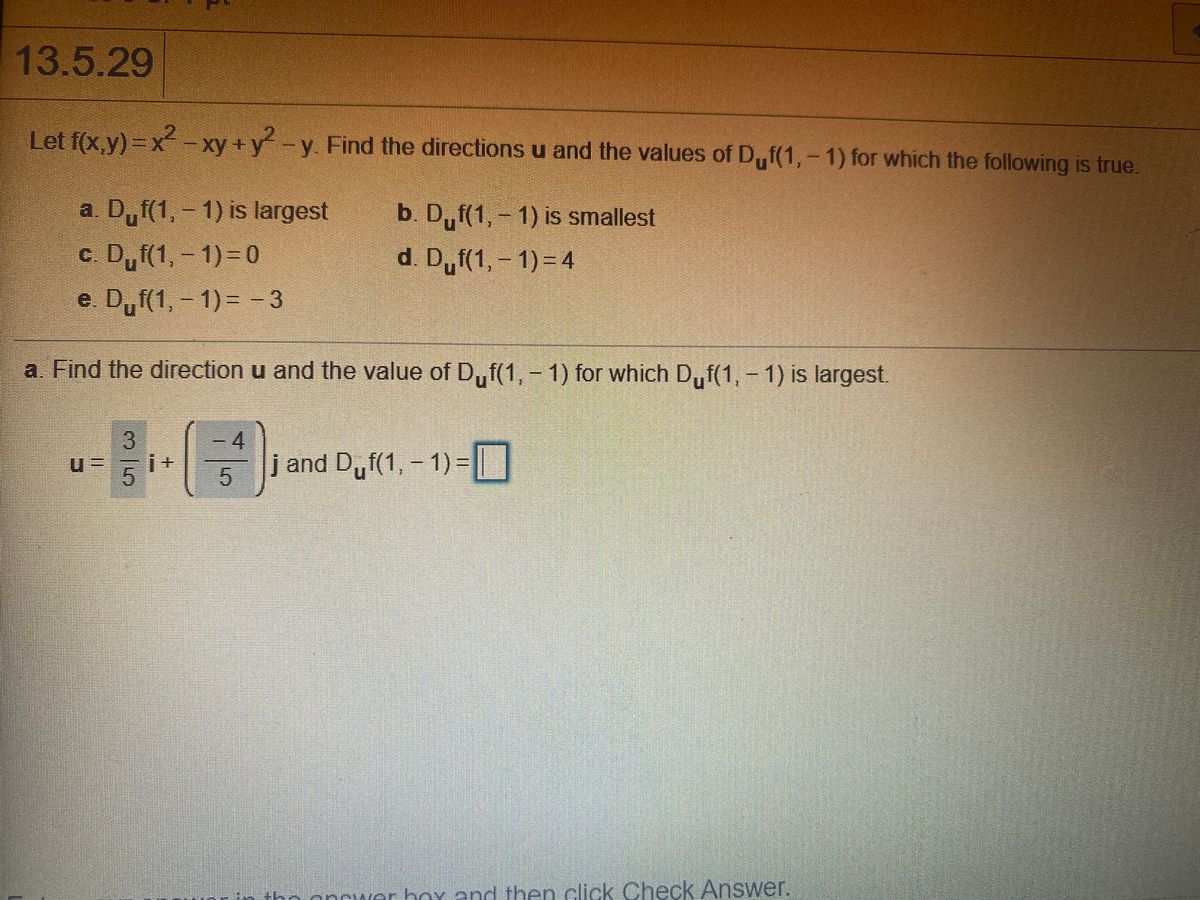
Answered Let F X Y X Xy Y Y Find The Bartleby

Asymptotics Wkb Method Sheet 5

Natural Logarithm Wikipedia
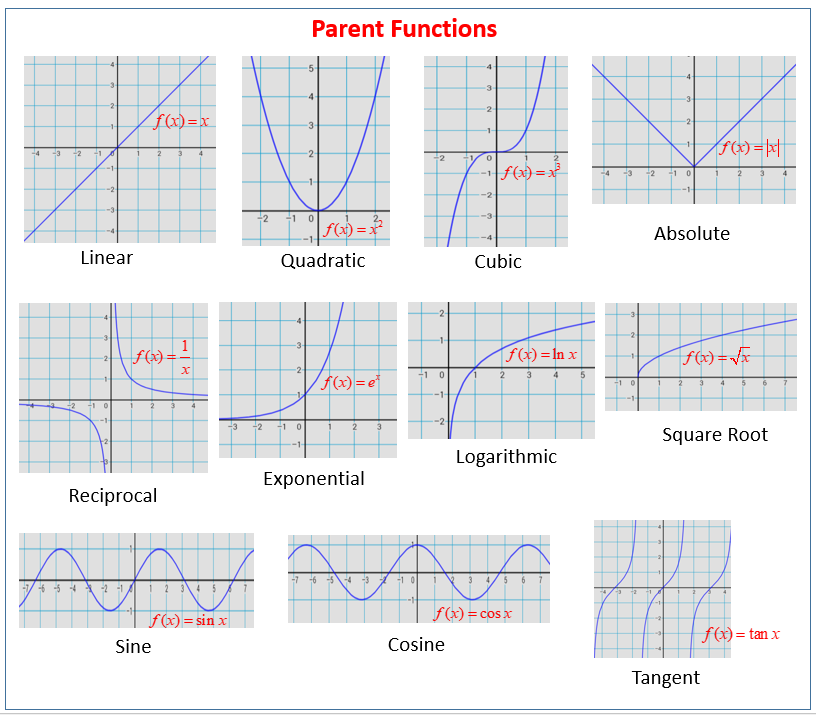
Parent Functions And Their Graphs Video Lessons Examples And Solutions

Calculus Assessment 13 Question Sheet Calculus Exercises 13 Please Hand In Your Studocu

成果及论文 张凤娇课题组

If Z F X Y Where X E U E V Brainly In
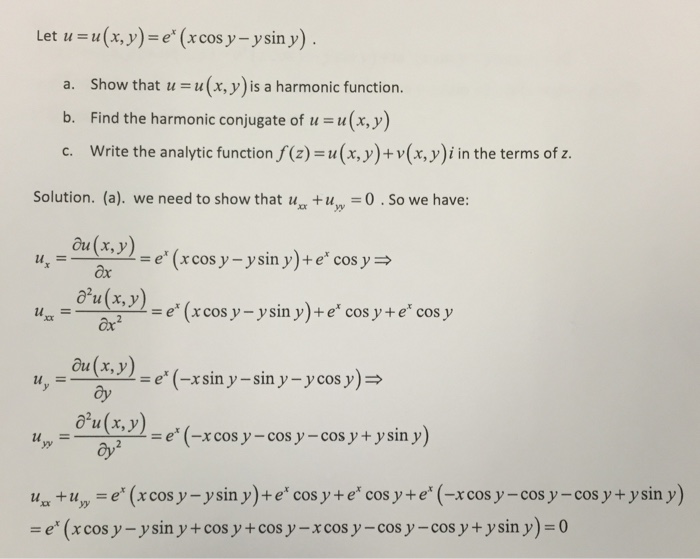
Solved Let U U X Y E X X Cos Y Y Sin Y Show Th Chegg Com

Finding Features Of Quadratic Functions Video Khan Academy
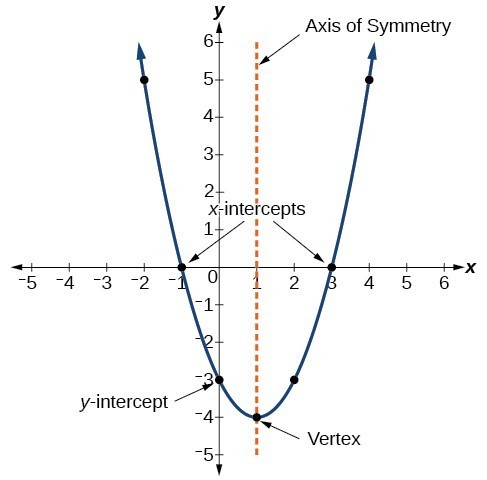
Characteristics Of Parabolas College Algebra

Jacobians New
Differentiation Of Composite Function Let Z F X Y Possesses Continuous Partial Derivatives And Let X G T Y H T Possess Continuous Ppt Download

Solved 1 Draw The Tree Diagram For The Chainrule And Wr Chegg Com

Automated Shape Differentiation In The Unified Form Language Springerlink

E Mathematical Constant Wikipedia

Nos Taylormade Owner Pennant 10 X16 Red Blue Sailcloth E F G I N O Q U Y X Bp1 Ebay

Chain Rule Derivative Logarithm

Pdf Of X Y Z Where X Y Z Are Independent U 0 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange
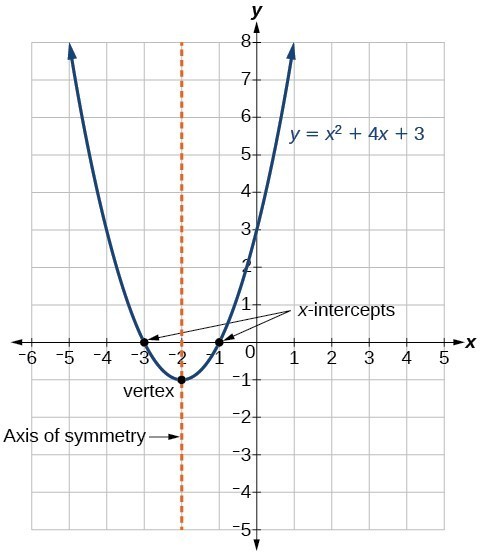
Characteristics Of Parabolas College Algebra

Three Line Ab Cd And Ef Meet At Point O Forming Angles As Shown In The Fig Find The Value Of X Y Z Brainly In
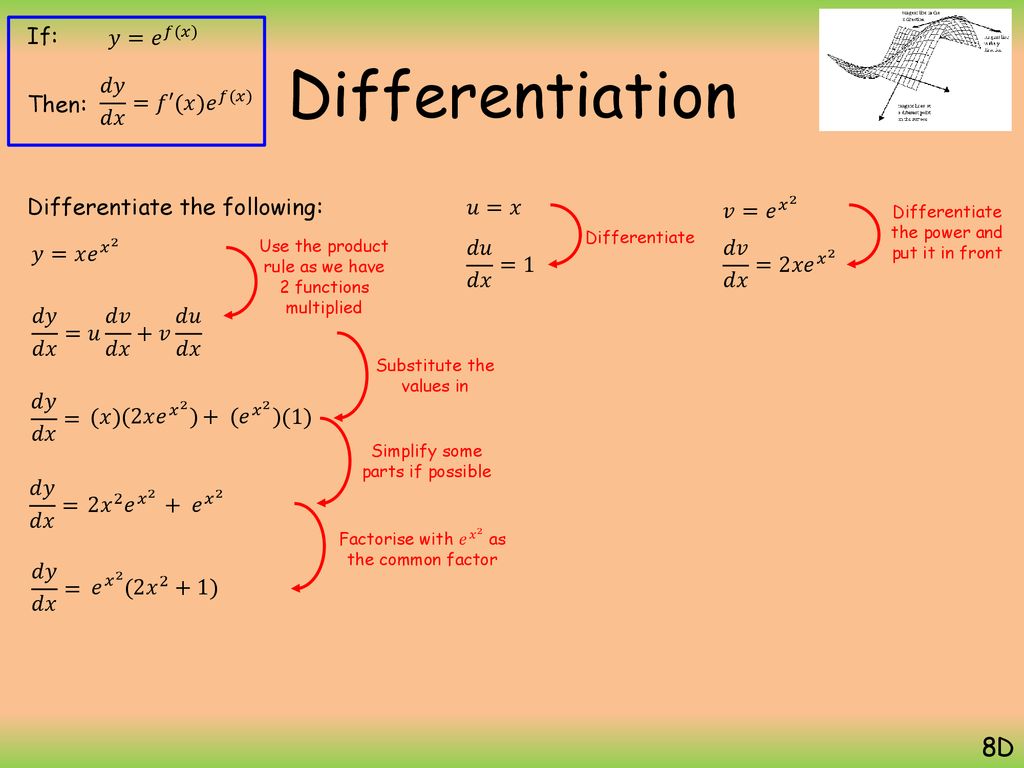
Differentiation Ppt Download




