Vv Bv Ux
Hence λf(v,v) = 0 Since q(v) = f(v,v) 6= 0 it follows that λ = 0 so w = 0 Proof of the theorem We use induction on dim(V) = n If n = 1 then the theorem is true, since any 1×1 matrix is diagonal So suppose the result holds for vector spaces of dimension less than n = dim(V) If f(v,v) = 0 for every v ∈ V then using Theorem 53 for any basis B we have fB) =)) = 0.
Vv bv ux. Data from War over Holland National Norwegian Aviation Museum Thulinista Hornetiin General characteristics Crew 2 Length 925 m (30 ft 4 in) Wingspan 1250 m (41 ft 0 in) Height 33 m (10 ft 10 in) Wing area 3930 m 2 (4230 sq ft) Empty weight 1,9 kg (4,233 lb) Max takeoff weight 2,145 kg (4,729 lb) Powerplant 1 × Rolls Royce Kestrel VIIb V12 liquidcooled piston engine,. Prove the following vector space properties using the axioms of a vector space the cancellation law, the zero vector is unique, the additive inverse is unique, etc. Example 3 (Continued) Find the dot product of u and v u · v = a1 a2 b1 b2 u · v = (6)(3) (2)(5) u · v = 18 – 10 u · v = 8 Find the angle between the vectors cos 1 uv uv θ − ⋅ = () cos 1 8 210 34 θ= − θ≈cos −1 θ≈° 775.
U = 2i 4j k, v = 3i j 2k. Find A) (u X V) * W B) V *(u X W) C) U * (w X V) D) (u X V) * V This problem has been solved!. XZY Y hCg Xb V'\^V'acf6 Ó2db`V'j)V'aª g \ gfs\^CV i aqXZ C f^\ca x W}\ acV db B\^CV ¨ ¦¢6 & '¢sdb B\^V Ca^V}W'd)eChg \cgd)eCV'a \c_Xb\ X V'W'\cf \cCV Ca^d _Xbi8Xb\cg d e db ge8 d a^ XZ\^gd)eo _ d f^V}V2\^g fªbW'd eCf^ghCV'a XsYg eV d)e @j V'a^\cgW'V'f6.
Ave ~ Avãj vn gn v¤§v` kn x` jvn L vb gv` vbx Formatted Justified, Indent First line 0", Tabs 425", Right mbœv‡Z ivmj @ I Pvi Bgv‡gi Ae¯vb 2 mby v‡Z i vmj @ I Pvi Bgv‡ gi Ae¯’vb c KvkK Ave`j−vn, Avngv`j−vn I bvQi“jvn Mš ¯ Z ¡ †jLK KZK msiw¶Z. Then FX is the collection of functions from X into F Define (f g)(x) = f(x)g(x) and (af)(x) = af(x), for f,g ∈ V and a ∈ F 13 Other properties of a. Problem Set 2 Solutions 3 MIT Professor Gerbrand Ceder Fall 03 1 P S(U, V) dS = dU dV T T Problem 11 Variables here are U and V and intensive variables are 1 and P T T To go to 1 T as a natural variables take the Legendre transform by subtracting U from S T.
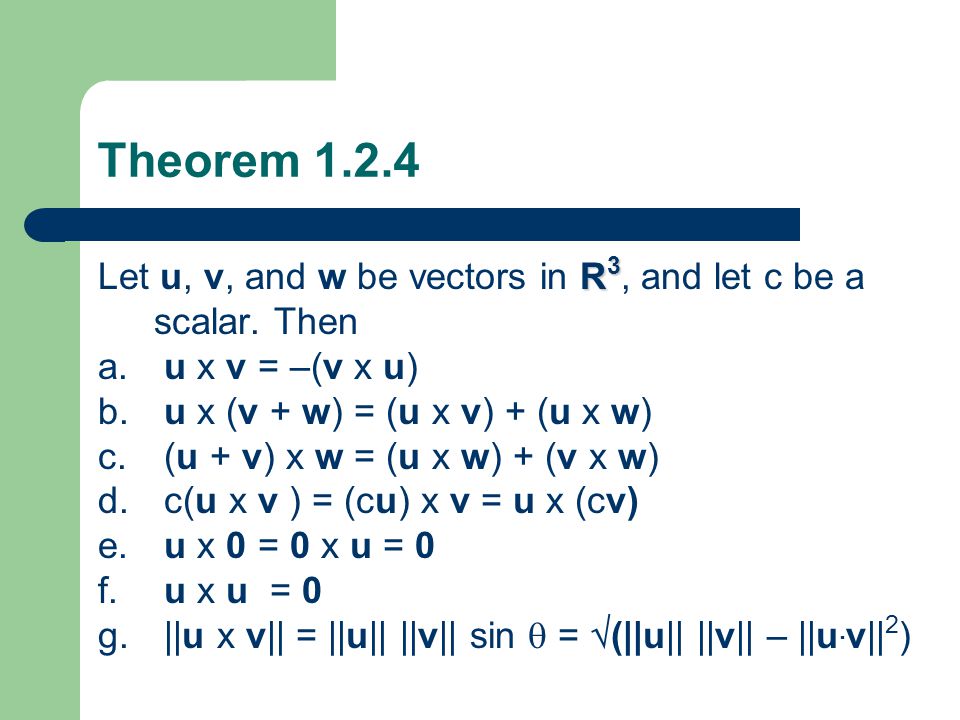
Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Nevada, Reno Reno, NV 557 Email Qipingataolcom Website wwwcseunredu/~yanq I came to the US. Sep 26, 09 · div ( u cross v) = v dot grad ( u ) u dot grad ( v) where v and u is a vector The product rule doesn't seem working The "product rule" in vector calculus is different to the product rule for scalar functions The "vector product rule" depends on type of product you are dealing with (eg cross, scalar) and the type of operator that you are dealing with (eg divergence, curl) in. U¢(v £w) = w ¢(u£v) = v ¢(w £u) (interchanging two rows changes the sign of a determinant, thus interchanging two rows twice leads to the same determinant Theorem 4 (a) If u = (u1;u2) and v = (v1;v2) are vectors in 2space, then the area A of the parallelogram determined by the vectors A = fl fl fl fldet µ u1 u2 v1 v2 ¶fl fl fl fl.
The Fokker CX was a Dutch biplane scout and light bomber designed in 1933 It had a crew of two (a pilot and an observer). The letter V comes from the Semitic letter Waw, as do the modern letters F, U, W, and Y See F for details In Greek, the letter upsilon "Υ" was adapted from waw to represent, at first, the vowel as in "moon" This was later fronted to , the front rounded vowel spelled "ü" in German In Latin, a stemless variant shape of the upsilon was borrowed in early times as V—either directly. Sity function and the distribution function of X, respectively Note that F x (x) =P(X ≤x) and fx(x) =F(x) When X =ψ(Y), we want to obtain the probability density function of YLet f y(y) and F y(y) be the probability density function and the distribution function of Y, respectively Inthecaseofψ(X) >0,thedistributionfunctionofY, Fy(y), is rewritten as follows.
CV åq`Vk, X gddhXhghX^^ g hb `V` Xåhd_ @ik ZVh ^b shi gedgdWcdghr U cVe^gVa shi `c^Yi ZX^\^bq_ \aVc^b Wqhr Xfcqb Wd\ghXccdbi edfimc^ä HV efdhå\c^^ bcdY^k ah å c efdghd im^a ^gh^cVb, gdZf\Vo^bgå X shd_ `c^Y, cd ^ Xgb gfZlb ghfb^agå Zdgh^YVhr ^k X gXdb a^mcdb kd\Zc^^ g =dYdb MV` mhd edXfrh bd^b gadXVb «Aga^ Xq WiZh. 2 Norm = length kvk= p v v u is a unit vector if kuk= 1 If v 6= 0 then u = 1 kvk v is a unit vector positivelyproportional to v examples!. Ot • U 00 «t B « H O 0 » ** •H 4J « V u n » wo u X*H ^«tf CO C O 0 0 O W 0 •C K 0 B • J B j* V •H ^ ** » u u 0 fl 0 B v M y C ** ** 1 B o i tr « • "M *> 0 • » o t* e ** U O M 0 w o a) n "0 b • • 0 * 0 B *• »• « • (• « o V V 1 iH >O H O (A H « Ui • t) «4wl ^ U *> 4C U «J « (J 0 0 V) B.
U(x,y) and v(x,y) of the function, show that these satisfy the CauchyRiemann equations, and find f′(z) in terms of z Solution By definition, f(z) = eiz = eixe−y = e−ycosxisinx Therefore, u(x,y) = e−y cosx v(x,y) = e−y sinx These are continuous functions at all (x,y) ∈ R2Now, ∂u ∂x = −e−y sinx = ∂v ∂y ∂u ∂y. XtypeRS { H O ɂ́A p ̉ n p J V v A u X { H ́A p R f B V i ̂ g p ߂ ܂ B ȏC E σX h ɕt փW ~ ␅ C ̏ ɍœK ȃJ V v ( ܂ z Ȃ ) ł B. P R I O R I T Y D a t e 0 2 / 2 1 / 2 0 0 7.
3) and v = (v 1,v 2,v 3), then the dot product of u and v is u · v = u 1v 1 u 2v 2 u 3v 3 For instance, the dot product of u = i − 2 j − 3 k and v = 2 j − k is u · v = 1 · 0(−2) · 2(−3)(−1) = −1 Properties of the Dot Product Let u, v, and w be three vectors and let c be a real number Then u · v =. 3 Cross product De nition 31 Let ~vand w~be two vectors in R3The cross product of ~vand w~, denoted ~v w~, is the vector de ned as follows the length of. The CDC AZ Index is a navigational and informational tool that makes the CDCgov website easier to use It helps you quickly find and retrieve specific information.
U= (ST)u= S(Tu) = S(Tv) = (ST)v= v Hence u= v Thus Tis injective, as desired Exercise 3B21 Suppose Wis nitedimensional and T2L(V;W)Prove that Tis surjective if and only if there exists S2L(W;V) such that TSis the identity map on V Proof First suppose T is surjective Thus W, which equals rangeT is nitedimensional (by Proposition 322) Let w. Begin privacyenhanced message proctype 01,micclear originatorname webmaster@wwwsecgov originatorkeyasymmetric. To check that uv = v u (axiom 3) for W because this holds for all vectors in V and consequently holds for all vectors in W Likewise, axioms 4, 7, 8, 9 and 10 are inherited by W from V Thus to show that W is a subspace of a vector space V (and hence that W is a vector space), only axioms 1, 2, 5 and 6 need to be verified The.
For each vector u 2 V, the norm (also called the length) of u is deflned as the number kuk= p hu;ui If kuk = 1, we call u a unit vector and u is said to be normalized For any nonzero vector v 2 V, we have the unit vector v^ = 1 kvk v This process is called normalizing v Let B = u1;u2;;un be a basis of an ndimensional inner product space VFor vectors u;v 2 V, write. Vector addition can be thought of as a map V ×V → V, mapping two vectors u,v ∈ V to their sum uv ∈ V Scalar multiplication can be described as a map F×V → V, which assigns to a scalar a ∈ F and a vector v ∈ V a new vector av Definition 1 A vector space over F is a set V together with the operations of addition. But clearly this is true set theoretically (if u 2W 1 and u 2W 2, then of course u 2W 1\W 2), ie W 1 \W 2 is the largest subset of V contained in both W 1 and W 2Since we have shown in the lectures that W 1 \W 2 is also a subspace, we are done 3 Let W 1 and W 2 be subspaces of a vector space V Show that the following statements are equivalent (i) W 1 \W 2 = f0g (ii) If w.
%' %' W & % Ym^% V Y\ \%W\T % %' %' W vu}XVX& %DY v W T %^ ( W kY\ ^% y%D %D W £Y\ gT V Ym D ú^ g_ 0 yVX \W &(%DY0VX %e W Y VXW Ï úi =ÏX. Find the cross product u x v if u = 2i j 3k v = 4j 5k Solution We calculate = 17i 10j 8k If you need more help see the lecture notes for Math 103 B on matrices Exercises Find u x v when u = 3i j 2k, v = i k;. OMBAPPROVAL UNITEDSTATES SECURITIESANDEXCHANGECOMMISSION Washington,DC549 OMB Number ExpiresFebruary28,09 Estimated.
Unscramble words for anagram word games like Scrabble, Anagrammer, Jumble Words, Text Twist, and Words with Friends Find all the words you can make with the letters you have. V b v)v2W and c X v2S a vv= X v2S (ca v)v2W The set W is called the subspace generated by S, or spanned by S, and we write W= hSi De nition 17 1 A vector space V is nitely generated if V = hSifor some nite subset Sof V 2 A subsetP S of V is linearly independent over k if every equation n i=1 a iv i = 0, where a. 2 Let V be a vector space Define T V → V as T(v) = v for all v ∈ V Then T is a linear transformation, to be called the identity transformation of V 611 Properties of linear transformations Theorem 612 Let V and W be two vector spaces Suppose T V → W is a linear transformation Then 1 T(0) = 0 2 T(−v) = −T(v) for all v.
(b) V = Mm,n, all m× n matrices with entries in F (c) V = Pn, polynomials of degree at most n, ie, p(t) = a0 a1t antn, with a0,a1,,an ∈ F (d) V = FX Let X be any set;. The identity map I V → V is injective 3 The linear map T P(F) → P(F) given by T(p(z)) = z2p(z) is injective since nullT = {0} 3 RANGES 5 3 Ranges Definition 4 Let T V → W be a linear map The range of T, denoted by rangeT, is the subset of vectors of W that are in the image of T. 3 Show that if A is an m×n matrix, then the solution set V to the equation Ax = 0 is a subspace of Rn Solution A1) Let x1;x2 ∈ Rn be two solutions to the equation Ax = 0 (that is, x1;x2 ∈ V)Then x1 x2 ∈ Rn, and A(x1 x2) = Ax1 Ax2 = 00 = 0 Thus x1 x2 ∈ V M1) Let x1 ∈ V, k ∈ R Then kx1 ∈ Rn, and A(kx1) = k(Ax1) = k(0) = 0 Thus kx1 ∈ V as well Thus by the subspace.
V(x) = V(V > 0) for x > L Region III a Write the general solution to the Schrödinger equation for the regions I, II, III, assuming a solution with energy E < V (ie a bound state) b Write down the wavefunction matching conditions at the interface between regions I and II and between II and III d Use your answers to a c. (4) u(x,y) = u0, v(x,y) = v0 Once we have this, algebraic and geometric intuition will usually handle steps A and C, but for B we will need a formula it uses a determinant called the Jacobian, whose notation and definition are (5) ∂(x,y) ∂(u,v) = u x xv yu yv u=u u=u u=u v=v v=v v=v 0 1 2 0 1 2 Using it, the formula for the area element in the u,vsystem is (6) dA =. (a) ux v (b) v x u (c) V×V u (12, 1, 0) v(6, 9,o) Find u x v Determine if u x v is orthogonal to both u and v by finding the values below O Type here to Get more help from Chegg.
“main” 07/2/16 page 326 326 CHAPTER 4 Vector Spaces Define an inner product on V via11 a11 a12 a21 a22 b11 b12 b21 b22 = a11b11 a12b12 a21b21 a22b22 Show that S is an orthogonal basis for W Solution According to Example 4618, we already know that dimW=3Using. Fred E Szabo PhD, in The Linear Algebra Survival Guide, 15 Angle An angle is a measure of revolution, expressed in either degrees or radians An angle θ between two vectors u and v, expressed in radians, is the value of the function ArcCosθ where Cosθ is the cosine determined by u and v 1 revolution = 360 degrees = 2 π radians. Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor.
Apr 26, 07 · let u (v) = v (v 1) hence u (v (x)) = u (x^2) = x^2 (x^2 1) = x^4 x^2 = h (x) which is what we wished to yield alternatively h (x) = x^2 (x^2 1) let v (x) = x^2 1 let u (v) = v (v 1) hence u (v (x)) = u (x^2 1) = (x^2 1)*x^2 = x^4 x^2 = h (x) charlie. The DFW CIV, DFW CV, DFW CVI, and DFW F37 were a family of German reconnaissance aircraft first used in 1916 in World War IThey were conventionally configured biplanes with unequalspan unstaggered wings and seating for the pilot and observer in tandem, open cockpits Like the DFW CII before them, these aircraft seated the gunner to the rear and armed him with a machine gun. β , , θ γ= decrease in angle between lines a and b γθβ= – dv θ≈ d x = v,x γ= v,x – β σ= Eε τ= Gγ τ σ F M V.
See the answer Suppose u *(v x w) = 2 Find a) (u x v) * w b) v *(u x w) c) u * (w x v) d) (u x v) * v Best Answer 100% (1 rating) Previous question Next question Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our calculus problem solver and calculator. Jan 29, 09 · Solutions Midterm 1 Thursday , January 29th 09 Math 113 1 (a) (12 pts) For each of the following subsets of F3, determine whether it is a subspace of F3 i {(x 1,x 2,x 3) ∈ F3 x 1 2x 2 3x 3 = 0} This is a subspace of F3To handle this and part iv) at the same time,. (R ev ) SE C R E T F E D E R A L B U R E A U O F IN V E S T IG A T IO N b 2 < f y P r e c e d e n c e !.
Geometry Of R2 And R3 Dot And Cross Products Ppt Download
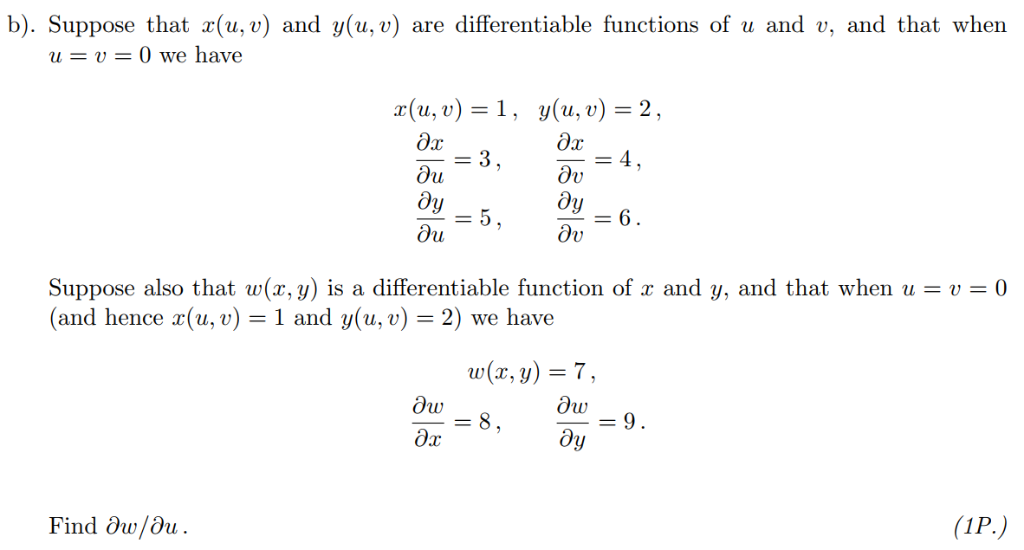
Solved Are Differentiable Functions Of U And V And That Chegg Com

14 7 Change Of Variables In Multiple Integrals Jacobians Mathematics Libretexts
Vv Bv Ux のギャラリー

Solved If F And G Are The Functions Whose Graphs

A Car Moves From X To Y With A Uniform Speed Vu And Returns To X

Decisions Under Uncertainty V Explicitly Consider Probability V

Consider A Transformation Tu V Xu V Yu

Solved Let U V Denote Vector Functions S A Second Order Chegg Com

More On Derivatives And Integrals Product Rule Chain

Solved Given The Function F X Y With X U V Au Bv Chegg Com

Solved 8 The Cross Product Of Two Vectors U X V X W I Chegg Com

Answered 2 Let U I 2 W3 N H V 2 Vs Bartleby

If F And G Are The Functions Whose Graphs Are Shown Let U X F X G X And V X F X G X A Find U 1 B Find V 5 Study Com

Computing Cross Products

Solved 1 Draw The Tree Diagram For The Chainrule And Wr Chegg Com

Integration By Parts Wikipedia

Vectors And The Geometry Of Space Monografias Com

A Question About The Pde U T Delta U Au Bvu Mathematics Stack Exchange
Consider The Following Relations From A To B Where Br A U V

Solved 1 Let 2 2 U A Find U And V B Find The V Chegg Com

Answered 2 A Solve The System U X 2y V Bartleby

Misc 16 If X Iy 3 U Iv Then Show That U X V Y
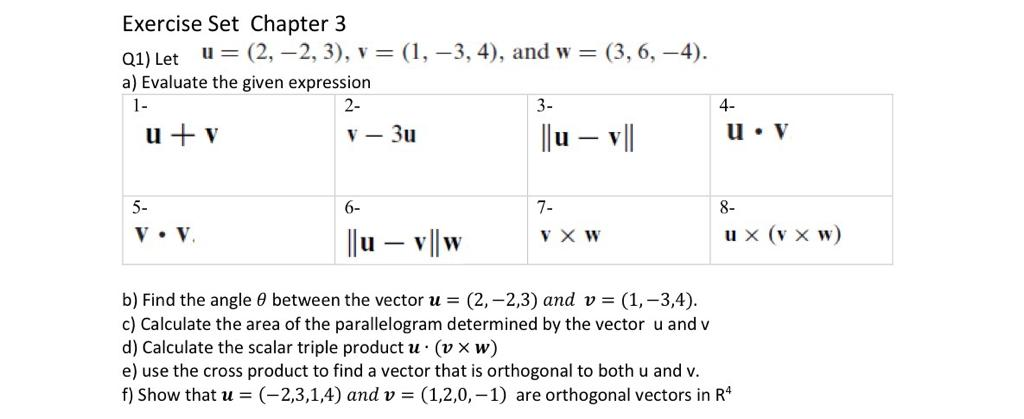
Solved Exercise Set Chapter 3 Q1 Let U 2 2 3 V Chegg Com

Misc 28 Find Derivative X 1 Tan X Chapter 13 Class 11
Solved If F And G Are The Functions Whose Graphs Are Shown Let U X F G X V X G F X And W X G G X Find Each Derivative If It Exi Course Hero
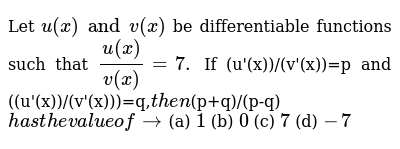
Let U X And V X Be Differentiable Functions Such That U X V

A Particle Is Moving With Speed V B Root X Along Positive X Axis Calculate The Speed Of The Particle At Time T T Assume That The Particle Is At Origin

If F X Log U X V X U 1 V 1 And U Prime 1 V Prime

Derive The Jacobian Of U And V With Respect To X And Y Mathematics Stack Exchange
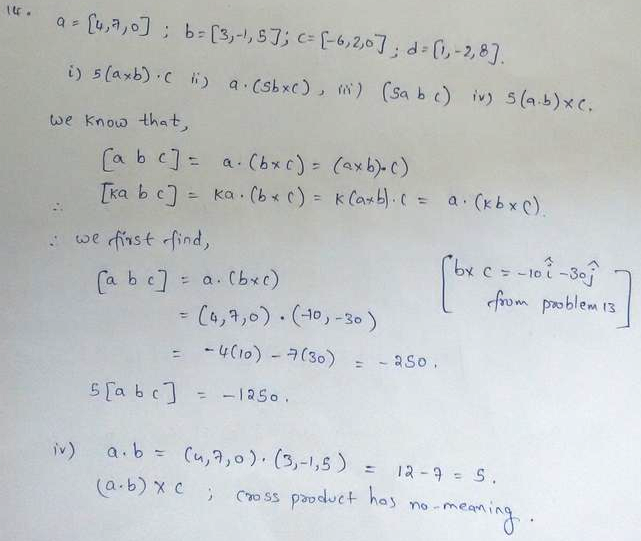
Assuming Sufficient Differentiability Show That A Curl U V Curl U Curl V B Div Curl V 0 C Curl Fv Grad F V F Curl V D Curl Grad F 0 E Div U V V Curl U U Curl V Homework Help And

Show That F U V 7u 4 U V 13u V Parametrizes The Plane 2x Y Z 8 Then A Calculate Tu Tv And Brainly Com

Vector Analysis By Alimkanwalimtinaa Issuu

Inner Product Spaces And Orthogonality
In Each Case Determine Whether U Is A Subspace Of R3 If So Prove It By Showing That Conditions 5 1 And 5 3 Hold Otherwise Show That One Of Course Hero
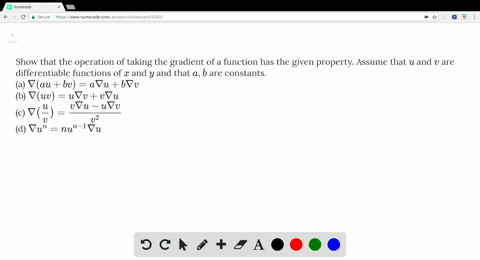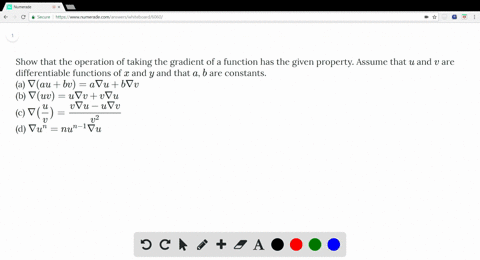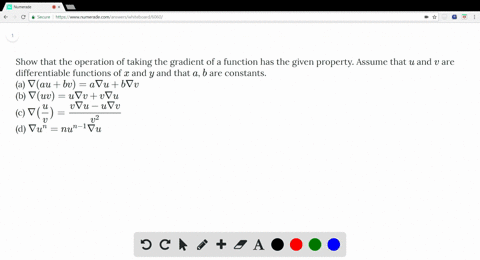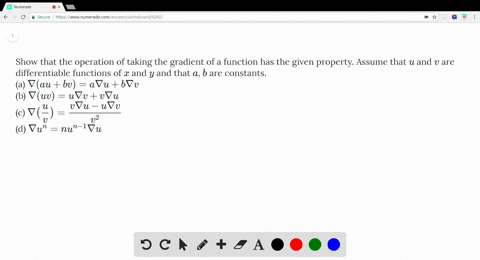
Solved Show That The Operation Of Taking The Grad

Solved Suppose That U U X T And V V X T Have Parti Chegg Com

Answered 18 Cross And Dot Products Show That If Bartleby

Answered 1 Suppose The Curves Parameterized By Bartleby

Consider A Transformation T U V X U V Y U V From R 2 To R 2 Suppose T Is A Linear Transformation T U V Au Bv Cu Dv Then The Derivative Ppt

Calculus Iii Vectors Prove That U X U X U X V Dot W U 2 U Dot V X W Learnmath

Vectors And The Geometry Of Space Monografias Com
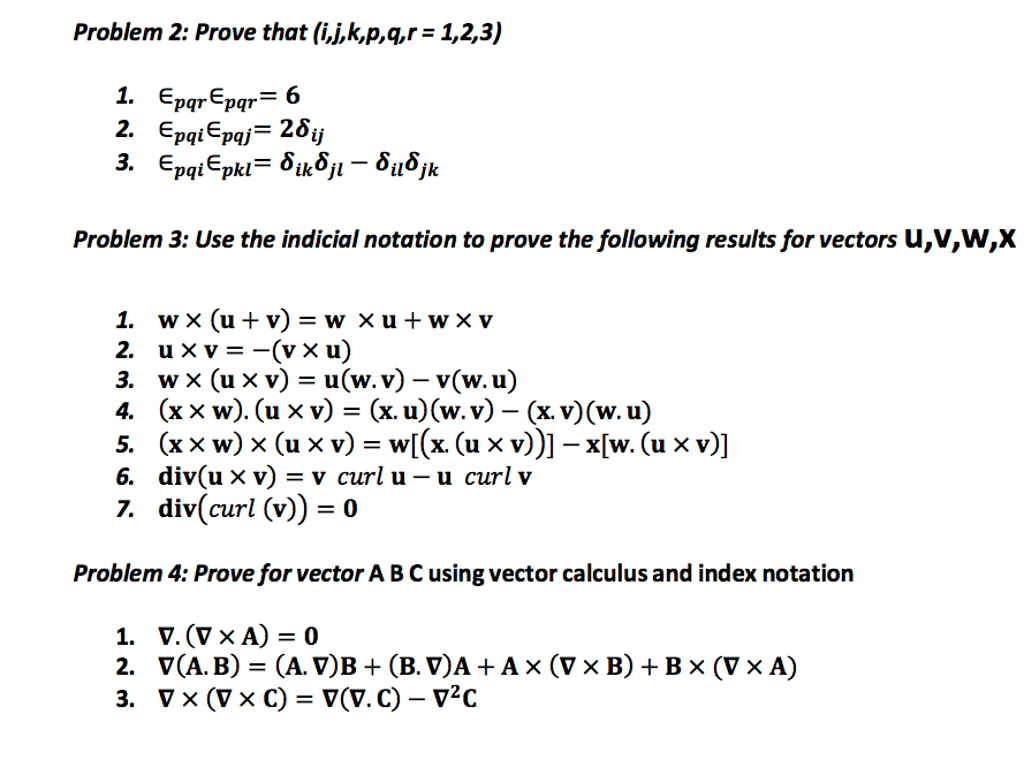
Solved Prove That I J K P Q R 1 2 3 Pqr Pqr Chegg Com

Vectors And The Geometry Of Space Monografias Com

If U A B And V A B And A B 2 Then U V Is Equal To Note A And B Are Vectors

Pdf Homework 1 9 8 9 9 Sojun Yun Academia Edu

Vectors Tutorial
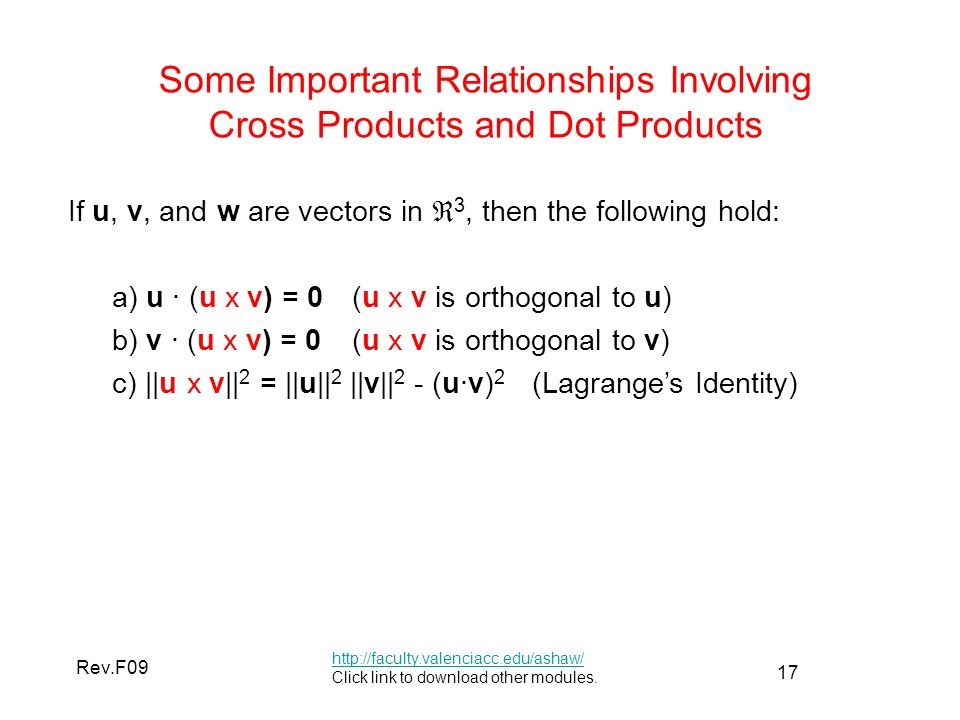
Vectors In 2 Space And 3 Space Ii Ppt Video Online Download
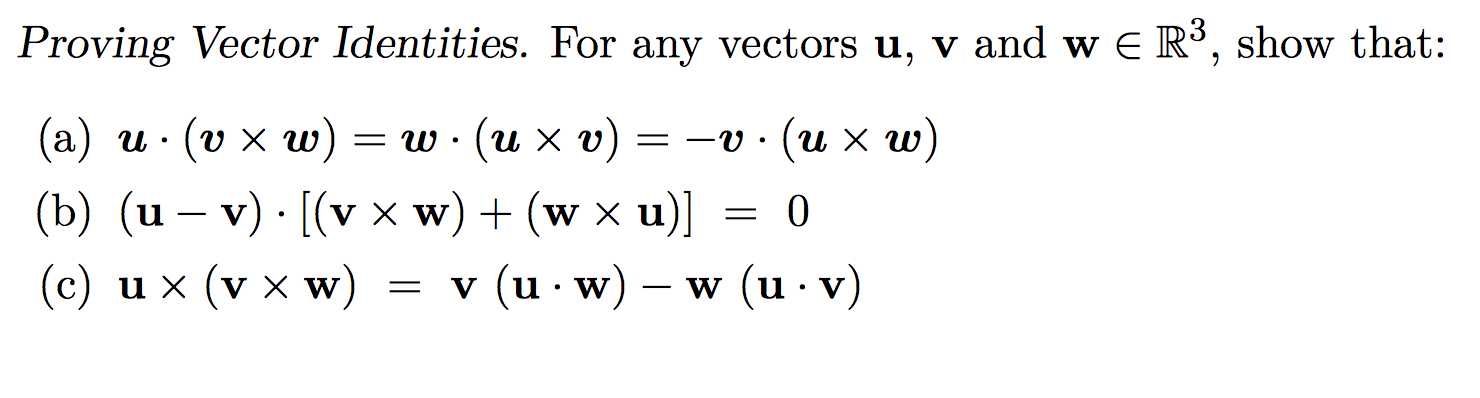
Solved Proving Vector Identities For Any Vectors U V An Chegg Com

Tableau Des Derivees

Find The Weak Solution Of The Conservation Law Mathematics Stack Exchange

Problem 3 Verify The Following Identities A U X Chegg Com
Vectors And The Geometry Of Space Monografias Com

Document

Mooc Program Test Basic Test 2 2 Programmer Sought

Electromagnetic Waves

Solved U 0 0 V 0 3 U 0 2 V 0 1 Find The Deriva Chegg Com

Solved 3 Consider The Vectors U 1 2 3 And V 1 1 Chegg Com

Document

7 Show That The Following Functions U X Y Monic Functions V X Y And Determine F Z U X Y Iv X Y Are Harmoni Homeworklib

What S The Difference Between Cos U V And Cos U Cos V Calculus
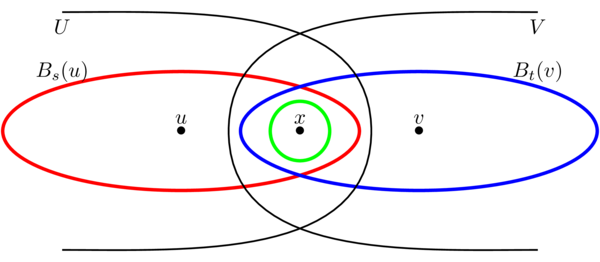
2 02 Bases Metric And Product Topologies

Vectors In 2 Space And 3 Space Ii Ppt Video Online Download

Answered Let F U V Be A Function Of Two Bartleby




